The quality of used water is subject to the requirements of the technological process and equipment type. Chemical plants use different water: River, artesian, filtered, koagulirovannuû, chilled, partially or totally obessolennuû, drinking etc.
Fresh natural water is used without further purification processes in the chemical industry in the primary processing of raw materials, for cooling products and devices and various subsidiary operations. In most cases, natural water is treated (demineralization) different techniques depending on the nature of impurities, and requirements, water production data requirements.
Water treatment process applied mechanical, physical, chemical and physico-chemical methods: Dodge, softening, Ion Exchange, obeskremnivanie and degassing. Drinking water, in addition, disinfect. In the above diagram, the (figure 16.1) the basic techniques for water treatment.
Brightening water is mainly the methods of deposition of impurities, released from water in the form of sludge. These methods are also called purification, as for the selection of impurities in water injected Special reagents. Deposition processes, used for the clarification of water, include coagulation, Liming and magnesium obeskremnivanie.
Under coagulation understand physical-chemical process of adhesion of colloidal particles and particulate formation microfase (flokul) Since then deposition. As reagents, called coagulants, usually apply sulfates Al.2(SO4)3 and FeSO4.
Improve coagulation effect is reached when adding flocculants (polyacrylamide, Active silicic acid, etc.). While accelerating the formation of flakes and improving their structure.
Created hlop′evidnuû a lot, consisting mainly of Al and Fe hydroxides and impurities, allot of water in ponds or special osvetlitelâh (residue in them supported in suspension flow coming from the bottom of the water), pressure or open filters and contact osvetlitelâh with loading of grain materials (quartz sand, crushed anthracite, expanded clay, šungizit, etc.), as well as skimming, gidrociklonah, precoat filters. For partial removal of coarse impurities and phytoplankton, from bloom reservoirs, apply mesh microfilters, flat and drum grid.
Liming water is to reduce alkalinity water desalt. At the same time reduced stiffness, salinity, concentrations of coarse impurities, iron compounds and silicic acid.
Reagent for this process is slaked lime Ca(OH)2, served as a suspension in water (lime milk). To improve the efficiency of removal of silicic acid in water add caustic magnesite (from 70 to 80 % MgO).
These processes, as a rule, combined and are conducted simultaneously in one device-osvetlitele. Final cleaning of sediment is carried out using the process of filtering. Depending on the size of the particles to be filtered and effective pore diameter particle retention can occur both in the extent of the filtering layer (adhesive bonding filtering), and on its surface (membranous filtration).
As filter materials mainly use quartz sand, crushed anthracite, sulfonated coal, pulp, Perlite, volcanic slags, expanded clay etc.
Umâgčeniem water is called its removal of calcium and magnesium compounds, contributing to the water hardness. One of the most effective ways of water softening is the lime-soda method in combination with phosphatic. Softening process is based on the following reactions:
1) processing of slaked lime to correct temporary hardness, remove iron ions and binding CO2:
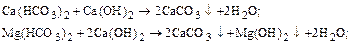
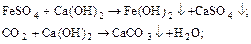
2) processing kaltsinirovannoj soda to eliminate permanent hardness:
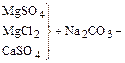
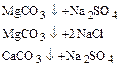
3) processing trinatrijfosfatom for more complete deposition cations Ca2+ and Mg2+:
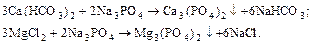
The solubility of calcium phosphates and magnesium is negligible, that provides high performance phosphate method.
Currently for softening, desalination and water obeskremnivaniâ is widely applied method of ion exchange. Its essence is, that is a solid ion exchanger-absorbs electrolyte of positive or negative ions in Exchange for an equivalent amount of other, same charged, ions. In accordance with the sign of the charge exchange ions distinguish cation and anion exchangers.
The cation is practically insoluble in water substances, representing a salt or acid anion, contributing to the insolubility in water; cation same (or sodium hydrogen) able to join under certain conditions in the Exchange reaction with cation solution, in which the cation exchanger. Cation, respectively called .33na-kationitami and H-kationitami.
Anion-base or salt with a solid insoluble cation. Anion exchangers contain movable hydroxyl group (Oh-anion exchangers).
As the Na-cation used Aluminium silicates: glauconite, zeolite, permutit etc.; as H-cation-sulfonated coal, synthetic resins; to OH-anionitam are artificial resin compound, for example, urea.
Ion exchange between the solution and the exchanger has the character of a heterogeneous chemical reactions. It should be noted, that impurities, removed from the water by the method of ion exchange, do not form a precipitate, and that this treatment does not require continuous dosing.
An important characteristic of ion exchange capacity is, indicates the ability of the resin bed to absorb a certain amount of ions in the circumstances. Exchange capacity determines the duration of the work's cycle ionitovyh filters. When it reaches the specified limit, exchange capacity ion conducting recovery process (Ion Exchange, held in reverse order).
Figure 16.2 the scheme of water softeners with consistent application of H-kationirovaniâ and OH-anioniro-Bani. When passing water through a cation exchanger it is freed from calcium and magnesium ions in H-kationitovom filter 1, and then in the anion filter 2 anions are removed from the. Then the water passes through the degasser 3, where it is released from the oxygen and carbon dioxide, continue through the collection 4 to the consumer. For regeneration of the filter 1 provides visitors with sulfuric acid, in filter 2 -sodium hydroxide solution.
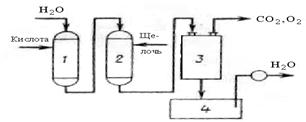
1 -kationitovyj filter; 2 -anionitovyj filter;
3 -degassing device; 4 -the collection of water
Figure 16.2 -Diagram of an apparatus for water softening
An important part of an integrated technological process water treatment water-removal of dissolved gases. The presence of gases in water due to sorption and dropping them as chemical reactions in the formation of impurities in natural water, and the advent of them during various stages of cleaning. These gases can be divided into chemically not interact (H2, O2, CH4) and chemically interact with water and its impurities (NH3, CO2 Cl2), as well as the corrosive (O2, CO2, NH3, Cl2,H2S) and inert (N2, H2, CH4). The concentration of gases in water depends on many factors; the main of them is the physical nature of gas, degree of saturation, the system pressure and temperature of water.
The main way to remove dissolved gases from the water-desorption (thermal deaeration). Its principle is to establish contact with the steam water, in which the partial pressure of a gas, to be removed from the water, close to zero, that is a necessary condition for the process of desorption. This process is carried out mainly in deaèratorah (vacuum, atmospheric, constant pressure), that by way of the distribution of water and steam are divided into ink, tape and bubble. Interval working pressure vacuum ranges from deaèratorah 0,0075 to 0,05 MPA.
In some cases, using chemical methods. So, to remove the oxygen in water Add strong reductants (for example, the sodium sulfite); H removal2S chlorinate water.
To obtain the distillate, needed to produce chemically pure reactants, medicinal drugs, various analyses, in laboratory practice apply thermal desalination of water. This process is carried out in evaporators boiling type. If this distillate is produced mainly from water, previously softened on ionitovyh filters.
The presence in water of pathogens and viruses makes it unfit for domestic consumption, and the presence in water of certain kinds of microorganisms (for example, filamentous, zooglejnyh, sulphatereducing bacteria, Iron bacterium) causes fouling, and sometimes the destruction of pipelines and equipment. Disinfection of water exercise, as a rule, chlorination of its liquid or gaseous CL2, gipohloritami-NaClO, Ca(ClO)2, ClO2. Also used for water disinfection, ozone and ultraviolet irradiation.
Water and sewer costs ranging from 5 to
15 % of the cost of chemical enterprises.
The air in the chemical industry use, basically, as raw materials or as a reagent in technological processes, as well as for energy purposes (as an oxidizer to obtain thermal energy by burning various fuels).
Air, applied as a reagent, exposed depending on the nature of the production of special cleaning from dust, moisture and contact poison. It is also used as a coolant and refrigerant in industrial processes. Compressed air is widely used in various mixing faucets bubbling liquids and slurries, in the jets-for spraying liquids into reactors and facilities.
Pure oxygen, secreted by the rectification of liquid air, usually used for oxygen melting of metals, in the blast furnace process, etc..






